
page 14
| HAMADA BOILER WEB CATALOGUE |
| Fbc 3 |

page 16
 page 14 |
|
 page 16 |
Fluidized Bed Combustion Technology(2) |
PRINCIPLE OF FLUIDIZATION |
of the in-bed tubes immersed in the sand bed is 5-6 times higher than that of the conventional convection tube bank area. If design of boiler requires 30 m2 for convection area to generate 1000 Kg of steam per hour, we can safely take 1/6 of it or 5 m2 to generate 1000 Kg of steam from the immersed in-bed tube area. The fluidizing air enters through air distributors mounted on a flat base plate. The bed material is silica sand having a mean size of 0.9 mm (#3). Bed depth is about 400 mm. |
|
|
Start-up of the bed is achieved by the firing of an above bed distillate coal layer, which is lit by small quantity of oil at the very start. Startup is normally achieved in 45 minutes from cold status. Hot starts normally are achieved in less than 10 minutes, 6 minutes of which is needed for purging to ensure there are no pockets of ignitable gas in the boiler passes. If the bed temperature is above 600 oC no oil fuel is needed to re-start the bed. Usually bed can maintain enough heat or above 600 oC for 1-2 hours. |
|
The average bed temperature varies between 950 oC at full load to 750 oC at minimum load. In fluidised bed operation bed temperature is monitored and is in fact a better indication of combustion condition than a flame scanner used for oil burner. |
|
The major proportion of the fuel is burnt within the bed, with the remainder burning in the free board zone or disengaging space above the bed. With the injection of overfire 2nd air into the free board zone, disengaging space temperature will rise higher than the temperature of the bed. The final gas temperature leaving the furnace will be similar to the bed temperature as the elevation in temperature due to free board combustion is partially offset by the heat transfer to the uncovered portion of in-bed tubes and cooling effect of the fresh air injection. |
|
|
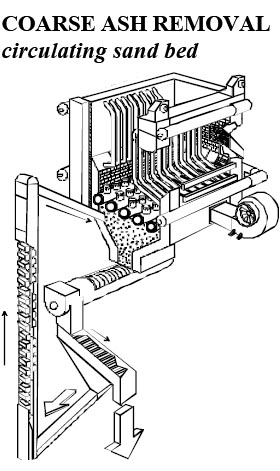 |
Fine coal is stored on the ground and normally flat conveyor system transport coal from the in-ground hopper to the silo mounted at the front of the boiler. The coal runs from the storage silo by gravity to the screw conveyor with variable speed gear motor, then the coal enters the furnace through an air swept spout. SOOTBLOWERS Soot blowers are not necessary to be installed as the combustion temperature of the fluidized bed is controlled at well below the ash fusion temperature and fly-ash entrained in the gases entering the convection tube banks are dry and non-adhering and possess a selfcleaning action. Coarse ash which is not elutriated from the bed must be removed. This material is removed continuously by means of circulating sand bed. We call this system as CIRCULATING BED. Air nozzles are screwed in to the multiple air distribution pipes instead of base plate which was used before. Because of this air distribution pipes, coarse ash can fall below the pipe level travelling downward in between the pipes and those materials will be discharged from the rotary valve below together with the silica sand onto the vibrating screen which will segregate those coarse ash and other foreign materials from the pure silica sand. Then the pure silica sand will be returned to the furnace |
 page 14 |
 Download This |
 page 16 |